A Dynamic En-route Filtering Schemefor Data Reporting in Wireless SensorNetworks |
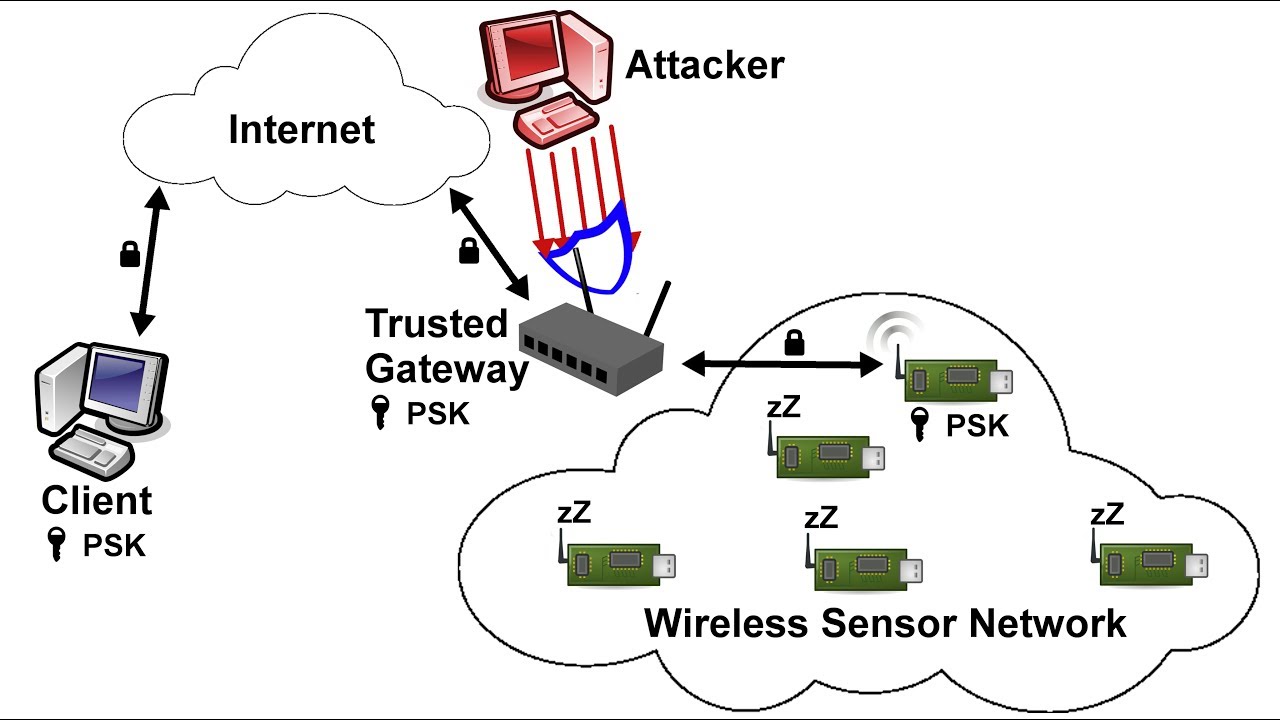
Abstract—In wireless sensor networks, adversaries can inject false data reports via compromised nodes and launch DoS attacks against legitimate reports. Recently, a number of filtering schemes against false reports have been proposed. However, they either lack strong filtering capacity or cannot support highly dynamic sensor networks very well. Moreover, few of them can deal with DoS attacks simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a dynamic en-route filtering scheme that addresses both false report injection and DoS attacks in wireless sensor networks. In our scheme, each
node has a hash chain of authentication keys used to endorse reports; meanwhile, a legitimate report should be authenticated by a certain number of nodes. First, each node disseminates its key to forwarding nodes. Then, after sending reports, the sending nodes disclose their keys, allowing the forwarding nodes to verify their reports. We design the Hill Climbing key dissemination approach that ensures the nodes closer to data sources have stronger filtering capacity. Moreover, we exploit the broadcast property of wireless communication to defeat DoS attacks and adopt multipath routing to deal with the topology changes of sensor networks. Simulation results show that compared to existing solutions, our scheme can drop false reports earlier with a lower memory requirement, especially in highly dynamic sensor networks.
Existing System
There are several existing scheme for filtering the false data injection, they are SEF, IHA, CCEF and LED have been proposed to address false report injection attacks and/or DoS attacks. And they have some limitation.
- SEF is independent of network topology, but it has limited filtering capacity and cannot prevent impersonating attacks on legitimate nodes.
- IHA has a drawback, that is, it must periodically establish multihop pairwise keys between nodes. Moreover, it asks for a fixed path between the base station and each cluster-head to transmit messages in both directions, which cannot be guaranteed due to the dynamic topology of sensor networks.
- CCEF also relies on the fixed paths as IHA does and it is even built on top of expensive public-key operations. More severely, it does not support en-route filtering.
- LEDS utilize location-based keys to filter false reports. They assume that sensor nodes can determine their locations in a short period of time. However, this is not practical, because many localization approaches take quite long and are also vulnerable to malicious attacks.
Disadvantages:
False Data injection attack in which an adversary injects the false data and makes the base station or relayed nodes resources drained.
In existing system SEF (Statistical En route Detection and Filtering) technique used in which all nodes have the same pre-determined probability to detect and filter false reports and its drawback is limited to fewer nodes.
In post deployment scheme each node establish a pair wise key in multihop nature and it can defend false data injection with a limited number of nodes. Its drawback is to transfer message base station and cluster vice versa. This is impractical in dynamic networks.
Proposed System
We propose a dynamic en-route filtering scheme to address both false report injection attacks and DoS attacks in wireless sensor networks. In our scheme, sensor nodes are organized into clusters. Each legitimate report should be validated by multiple message authentication codes (MACs), which are produced by sensing nodes using their own authentication keys. The authentication keys of each node are created from a hash chain. Before sending reports, nodes disseminate their keys to forwarding nodes using Hill Climbing approach. Then, they send reports in rounds.
In each round, every sensing node endorses its reports using a new key and then discloses the key to forwarding nodes. Using the disseminated and disclosed keys, the forwarding nodes can validate the reports. In our scheme, each node can monitor its neighbors by overhearing their broadcast, which prevents the compromised nodes from changing the reports. Report forwarding and key disclosure are repeatedly executed by each forwarding node at every hop, until the reports are dropped or delivered to the base station.
Advantages:
In the proposed system false data injection is detected with secret information and it is authenticated using MAC (Message Authentication Codes). In addition Hill Climbing approach is used to disseminate the secret keys in Sensor nodes.
Modules
- Pre-deployment phase.
- Post-deployment phase.
- Filtering phase.
- Report Forwarding Phase.
Software Requirements:
- Windows operating system 2000 and above
- JDK 1.6
Hardware Requirements:
- Hard Disk: 20GB and Above
- RAM: 512MB and Above
- Processor: Pentium III and Above

No comments:
Post a Comment